The concept of hyperlocal is not only the focus of attention but also the direction of development and successful functioning for many modern companies. At its core, hyperlocal refers to services and content tailored to a specific geographic location, often within a few kilometers of a user’s location.
With the widespread use of smartphones and real-time technologies, this hyperlocal business model is revolutionizing the way consumers interact with businesses in their immediate surroundings.
That is why hyperlocal is gaining so much traction today. The answer can be found in such things as digital convenience and relevance gained through localization.
Regardless of whether the service is as simple as getting groceries delivered or arranging for a cleaner or plumber at one’s home, hyperlocal platforms offer immediate utility.
And who should be paying attention?
Entrepreneurs, for new market opportunities. Developers, for creating location-aware platforms. Local businesses, for expanding reach. And for marketers, simply because ultra-targeted advertising is not something that can be achieved through any other means than by simultaneously reaching out to the audience and appealing to the brand’s values.
Table of Contents
A Basic Understanding of Hyperlocal Business Model
Hyperlocal means applications and solutions for areas focusing on users in very limited geographical areas. Some subdivisions can be clarified by just pointing to the fact that it operates in a vast field of industries:
Content: Neighborhood-specific blogs, news portals, or social groups.
Delivery: Same-day or within-hours delivery from local vendors.
Retail: Websites that assist in the purchasing or selling of products on local markets.
It is important to differentiate between the terms “local” and “hyperlocal.” The former might cover an entire town or city, while the latter focuses on specific towns or even neighborhoods or zip codes.
For example, one can have a local pizza delivery chain, but an h-App will tell you where you can order a pizza to be delivered within half an hour in your very neighborhood.
Real-world examples include:
- Zomato, Swiggy for food delivery.
- Urban Company for home services.
- Nextdoor for neighborhood engagement.
- Ola or Uber for instant ride-hailing in your area.
The Rise of the Hyperlocal Platforms
Hyperlocal services didn’t emerge overnight. They started with a simple newspaper’ advertisement section and expanded to comprehensive selling services fueled by today’s technology.
The rising use of the internet, smartphone devices and applications, and GPS solutions has made it possible to offer location-based services in real time.
Due to the Covid-19 restrictions, such as lockdowns and limitations on movements, people had to rely heavily on hyperlocal services for essentials such are food and medicine and services, leading to wider adoption with different age and geographical segments.
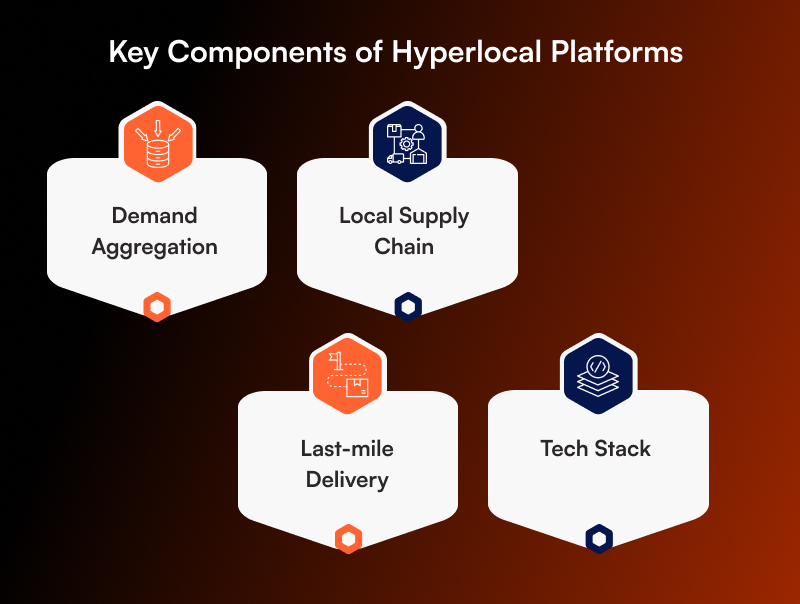
It is possible to define the following elements necessary for the efficient functioning of a Hyperlocal delivery services:
In this context, it is really imperative to focus on the definition of hyperlocal in order to establish the foundational components required for success.
Speaking of the target audience, define the focus area specifically, right down to the specific locations.
Demand Aggregation: The customer demand is to be collated through the use of applications or a platform.
Supply chain Localization: There is a need for vendors or freelancers to be engaged from the country of operation.
Logistics & Last-mile Delivery: Last-mile delivery plays an important role in meeting the required services in the shortest possible time.
Tech Stack Essentials:
Mobile apps (Android/iOS)
Maps and geolocation
APIs for logistics, payments, and CRM
Planning for vendor and inventory system Institutional Requirements & User Specifications for Vendor & Inventory Management Backend System.
Variant Types of Hyperlocal Services
Hyperlocal models span multiple sectors. Some of the most prominent include:
Hyperlocal Delivery
- Food (Swiggy, DoorDash)
- Grocery (Instacart, BigBasket)
- Medicine (PharmEasy)
Hyperlocal Home Services
- Cleaning services
- Repair and plumbing (Urban Company, TaskRabbit).
- At-home tutors
- Fitness trainers
Hyperlocal Marketplaces
Buy/sell apps like OLX and OfferUp
Community-based resale or rental apps
Hyperlocal News & Content
Some of the examples of such platforms are Citizen or Patch, which offer news based on your street or locality.
Technologies That Businesses Use for Hyperlocal Solutions
The ability to operate a hyperlocal business model depends more on the technology that it is embedded with. With the growing popularity of Apple, people these days pray for awesome app-based services on iOS and Android.
Locationality & Charting: Service locations are identified by Google Maps API, Mapbox, and Maps.
Order Tracking & Nearness Alerts: From the progress of the order to the time it reaches your doorstep. Some of the main benefits include, again, the ability to uncover usage patterns to be able to provide better offerings.
Payment & Logistics API Integration: For seamless checkouts and real-time logistics optimization.
Benefits of the Hyperlocal Model
Why are so many startups and legacy businesses shifting to hyperlocal? Because the benefits are compelling:
Swiftness: Services are quick, with the majority of them taking only one day or even hours.
Customer Retention: Local businesses build stronger customer trust and loyalty.
Targeted Space: Hyperlocal platforms involve users at that level that will be limited to their neighborhood or nearby areas.
Lower Cost of Fulfillment: Local fulfillment implies lower costs and expenses towards logistics and warehousing.
Challenges in Building Hyperlocal Solutions
Still, it does not come without challenges, as are presented by the hyperlocal model:
Inventory & Logistics: Stock control is one of the testing jobs in case of having many micro-locations for the store.
Vendor Onboarding: Ensuring quality, reliability, and compliance of local partners.
Data Privacy & Regulations: Storing and using location data comes with privacy concerns.
Scalability: A solution that proves effective when implemented in one region may not be the same when tried in other regions, mainly due to cultural differences, legal concerns, or some practical challenges.
Use Cases You Should Check on for Hyperlocal Services
Note that the following are some of the successful, far-reaching examples of hyperlocal business markets The
Dunzo: Dunzo a Bangalore-based startup that has created an application through which a person can order anything from any location in Bangalore.
BigBasket: To solve the problem of groceries and online product delivery and to compete with other online grocers successfully, it has leveraged hyperlocal warehouses to deliver groceries rapidly.
Nextdoor: A social platform connecting neighbors in local communities.
Urban Company: The Indian localized applications for service providing by professionals who can visit your home.
Postmates: On-demand delivery company operating exclusively in the United States, delivering anything from coffee to clothing, groceries, etc.
Future Trends of Hyperlocal Business Model
It may, therefore, be said that the hyperlocal revolution is only set off from its starting point. Such developments will be more defined and enhanced in the future to offer their services across the globe.
AI & Automation: There is the possibility for user prediction as well as route’ and recommendation’ prediction.
D&AVs: The two will revolutionize last-mile delivery to be much faster when it comes to fulfillment.
Tier II/III Cities & Rural Expansion: Huge untapped potential beyond metros.
Hyperlocal advertising: Locally tailored targeted advertising will be something that can be beneficial in creating better appeal in marketing.
Smart Cities & IoT Integration: Traffic control, home & building services, and smart infrastructure—all will be hyperlocal.
Final Takeaway
It is no longer just a buzzword; instead, Location-based ecommerce is a new way of configuring the types of services and commerce in the new digital environment. By catering to specific neighborhoods and user needs, businesses can offer speed, convenience, and trust like never before.
For entrepreneurs and developers, now is the time to invest in building hyperlocal platforms. With the right technology, strategic partnerships, and user-centric design, hyperlocal solutions can unlock tremendous value.
FAQs
Q1. What are the reasons to incorporate Hyperlocal Business Model?
This is the concept of dealing with goods, services, or content within a well-defined geographical location, and in most cases, only a few kilometers or within a neighborhood. It links the demand and the supplier within a particular region at a very fast and efficient rate with the help of GPS, Mobile applications, and maps.
Q2. How does a hyperlocal platform generate revenue?
It is a common practice with most hyper local platforms to monetize through several avenues, which include:
Commission fees from local vendors for each transaction.
Received charges from customers concerning delivery of the service.
Paid services such as suggested listings or upgrades to get a better placement for merchants.
Ads that are specific to particular stations, tracks, and the time of day or preferences of the users. Some may also provide B2B services such as transport or even provide applications to local businesses.
Q3. What technologies are essential for building a hyperlocal app?
The following are some of the technologies that should not be overlooked to support suitable hyperlocal app development:
Mobile app framework (Flutter, React Native, or native Android/iOS)
Geolocation APIs (Google Maps, Mapbox)
Real-time tracking and notifications
Payment gateway integration
Back-end management systems (for vendor onboarding, inventory, CRM)
Data analytics tools to enable personalization and demand forecasting
Q4. What are the biggest challenges in scaling a hyperlocal business?
Scaling hyperlocal businesses beyond one region involves:
Managing supply chains in diverse localities
Ensuring consistent service quality across vendors
Adhering to varying regional laws and data privacy regulations
Customizing user experiences for different locations What works in one area may not directly replicate in another due to local habits, competition, or logistics constraints.