The term “agent” is quite popular; you must have heard about it before. Whether it’s a travel agent, an estate agent, or a CIA/RAW agent as depicted in movies (which, of course, exist in real life as well).
However, here we will not be discussing any of those. That is not part of the syllabus at our AI agent development company. Instead, we are focusing on what are AI agents, and while covering this topic, we will go beyond the obvious.
What Are AI Agents?
The simple definition of agent is someone who acts on behalf of a company or another person to handle business or tasks.
But what is agent in AI? Well, it is a software or robotic entity that perceives its environment, makes intelligent decisions, and takes action to achieve specific goals.
In simple words, a software program that is doing some work on behalf of us. This work can be anything, depending on what purpose your AI agent is serving.
You must be thinking, how AI agents are then different from basic automation.
AI agents can learn, optimize, and even predict future outcomes based on past experiences. Yes, that makes the difference.
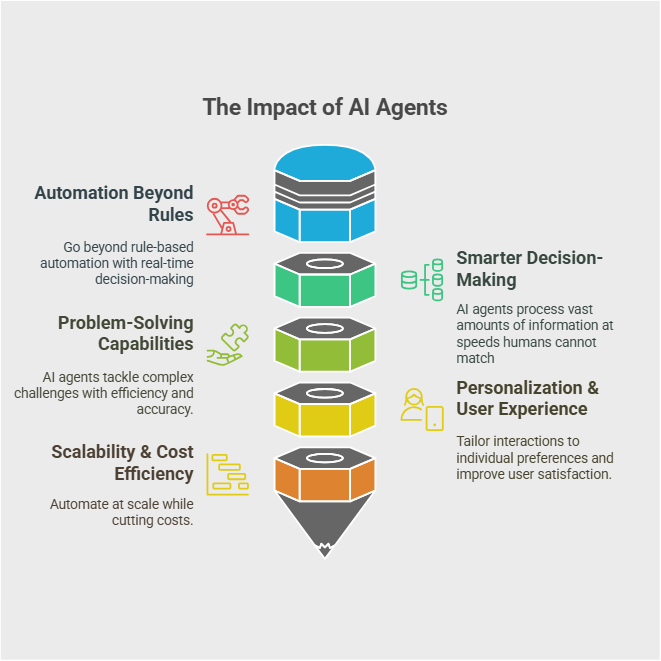
Why Do AI Agents Matter?
AI agents are making huge changes in all industries by making technology more autonomous, intelligent, and efficient.
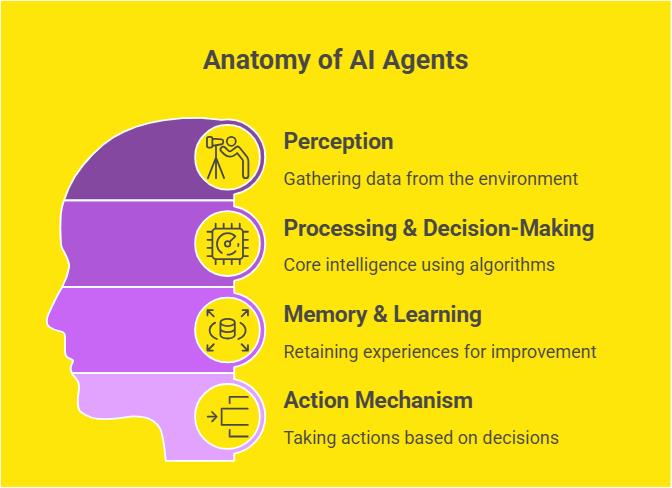
How AI Agents Works?
AI agents are built on four interconnected components: Perception, Processing & Decision-Making, Memory & Learning, and Action Mechanism.
Together, they enable AI agents to operate autonomously, adapt to new information, and perform tasks efficiently.
If you are seeing a virtual assistant, a self-driving car, or a recommendation system, these components form the foundation of intelligent behavior in AI systems.
Here are the four key components that enable AI agents to operate intelligently:
Perception (Sensors & Data Input)
AI agents gather data from their surroundings. This is achieved through sensors, APIs, or databases, which provide the agent with the necessary information to understand its environment.
The data collected can range from speech and images to numerical metrics. This data help AI agent to “perceive” the world in a way similar to how humans use their senses.
Processing & Decision-Making (AI Models & Algorithms)
Once the data is collected, the AI agent processes it using advanced algorithms and models. This is where the “intelligence” of the agent comes into play.
Technologies used here are Machine Learning Models, Deep Learning Networks, and Rule-Based Systems.
The AI agent evaluates the input data, applies its algorithms, and determines the best course of action based on its programming and objectives.
Memory & Learning (Knowledge Base & Training Data)
AI agents improve over time by retaining past experiences and learning from them. This is achieved through Knowledge Bases and Training Datasets.
Techniques like reinforcement learning allow the agent to learn by trial and error while neural networks help it adapt to new data and scenarios. This continuous learning process improve the agent’s performance and accuracy.
Action Mechanism (Actuators & Outputs)
After processing the data and making a decision, the AI agent takes action. This is accomplished through actuators or output mechanisms, which translate decisions into real-world outcomes.
The action mechanism makes sure that the agent’s decisions have a tangible impact on its environment.
What are Different Types of Agents in AI?
AI agents come in different types. Each designed for specific tasks and environments. Here are the primary types of agents in AI:
Simple Reflex Agents
These types of agents in AI respond to specific conditions based on predefined rules. They do not have memory or learning capabilities.
Example of these AI agent type is thermostat that turns the heater on when the temperature drops below a threshold.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
These intelligent agent in AI maintain an internal model of their environment which is not the case with simple reflex agents.
It allows them to make decisions based on both current and past data. A self-driving car that considers traffic patterns before making a turn is a perfect model based AI agents examples.
Goal-Based Agents
These types of agents in AI take actions to achieve specific objectives. They evaluate possible outcomes before making a decision. Goal based AI agent example is a chess-playing AI that plans multiple moves ahead to checkmate an opponent.
Utility-Based Agents
They aim to maximize a certain metric (utility). These types of agents in AI weigh different choices and select the one that provides the best outcome.
Utility based AI agent examples are stock trading bots that optimizes investments based on risk and potential profit.
Learning Agents
These agents improve their performance over time by learning from experience. They use techniques like reinforcement learning to adapt and make better decisions.
You must have heard AI assistants like Siri and Alexa. These are example of learning agent in AI that personalize responses based on user behavior.
Multi-Agent Systems
Some AI agents work collaboratively in groups, sharing information and coordinating actions. These systems are used in robotics, smart grids, and cybersecurity where multiple AI entities need to interact efficiently.
Are AI Agents Replacing Traditional Business Processes?
Yes, intelligent agent in AI is in action. Many businesses are utilizing them and getting the result they wanted. We recommend you as well to start your journey soon with an AI agent development company.
How are AI agents used in different industries?
Intelligent agent in ai is making a big impact in different fields by automating tasks and improving decision-making. Here’s how they help:
E-commerce & Retail:
AI agents analyze customer preferences and recommend products. This has helped ecommerce websites to increase their sales.
You can also build a custom AI agent that can predicts demand, restocks items automatically, and reduces waste. This keeps your businesses running smoothly.
Healthcare:
AI agents are helping doctors by analyzing medical images and test results. They are able to detect diseases early. Another application of AI in healthcare are smart systems. These AI systems track patient health and alert doctors in emergencies.
Finance & Banking:
AI agents scan transactions for suspicious activity. They are now detecting fraud and keeping your accounts safe.
These agents are also predicting stock trends and executes trades faster than humans.
Customer Service:
AI chatbots answer customer questions instantly. This is reducing wait times and increasing user satisfaction. Personalized responses based on user history is also a major AI agent application which is improving customer experience.
Smart Cities & IoT:
AI agents can optimize traffic lights to reduce congestion and save travel time. These systems can monitor infrastructure and predicts equipment failures before they happen.
How do AI agents work in autonomous systems?
AI agent is the reason we see self-driving cars, robots, and smart devices today. These knowledge based agent in AI allow these systems to operate independently and make decisions in real time. Here’s how AI agents are working in autonomous systems:
Self-Driving Cars:
AI agents analyze road conditions, detect obstacles, and make split-second driving decisions. Advanced learning systems help these cars improve navigation and avoid accidents.
Drones & Robotics:
AI-powered drones use cameras and sensors to perform tasks like aerial surveys and search and rescue missions. AI robots assist in manufacturing, warehouses, and even surgeries with high precision.
Smart Homes & IoT:
AI agents control home devices, adjusting lighting, temperature, and security based on user preferences. AI agents in IoT networks improves energy efficiency and home automation.
The Real Challenges of AI Agents No One Talks About This Enough
Here are some key challenges of AI agents that often don’t get enough attention:
Bias & Fairness Issues – AI agents can inherit biases from training data. This can lead to unfair or incorrect decisions in hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
Lack of Explainability – Many AI agents work like “black boxes”. They can make difficult decisions that even experts struggle to explain. This lack of transparency raises trust issues.
Security & Ethical Risks – AI agents can be exploited for cyberattacks, misinformation, and deepfakes.
Energy Consumption & Scalability – Training and running AI models require immense computational power. This can lead to high energy consumption and carbon footprints.
Regulatory Uncertainty – Governments are still figuring out how to regulate AI effectively. However, there are some laws that has been established. The European Commission introduced the first-ever EU artificial intelligence law in April 2021.
Difference Between AI Agents vs AI Chatbots
Most people confuse AI agents with chatbots. But there are differences. A chatbot is like a receptionist – it follows predefined responses.
An AI agent is more like a manager. It makes decisions, organizes tasks, and learns from new situations. Here’s why they’re not the same:
| Feature | AI Chatbots | AI Agents |
| Main Function | Responds to user input | Can make autonomous decisions |
| Intelligence Level | Basic NLP-based responses | Learns & adapts over time |
| Scope of Use | Limited to conversations | Can function in various fields |
All You Should Know About AI Agents vs LLMs
Another common confusion that people have is what is the difference between AI agents and LLMs (Large Language Models). Here is what you should know about LLMs and AI agents:
| Parameters | AI Models | LLMs |
| Built on AI Models? | Yes, AI agents integrate multiple AI models (ML, deep learning, reinforcement learning, NLP, etc.) for decision-making and action. | No, LLMs are AI models themselves, primarily designed for language generation and understanding |
| Autonomy | Can operate independently. Able to make decisions and take actions on their own. | Requires human input to generate responses and cannot take real world actions. |
| Purpose | Designed to perceive, decide, and act toward achieving a goal. | Built primarily for language understanding and text generation. |
| Examples | Self-driving cars, AI assistants like Siri, AI-powered trading bots. | ChatGPT, Google Bard, GPT-4, Claude AI. |
| How They Work | Use perception (sensors/APIs), decision-making models, and action mechanisms. | Use deep learning and transformer-based architectures to generate text predictions. |
AI Agents are Overhyped Trend or the Future of Intelligent Automation?
Many times, AI agents are surrounded by hype. But do they truly have a transformative future or is it just another tech trend? Let’s understand this by going beyond the obvious:
Why some believe AI agents are overhyped?
There are many reasons for that. But one word answer is they are not overhyped but a work in progress.
Limited General Intelligence – AI agents today are still task specific and cannot think or reason like humans. At least as of now. However, they are growing fast and growing their own reasoning ability.
But as they show in science fiction, AI agents do not possess true consciousness or creativity yet.
High Dependence on Data – Their performance heavily relies on large datasets and training models. Inaccurate or biased data can lead to poor decision-making.
Challenges in Autonomy – AI agents can automate decision-making. But they still require human oversight in critical applications like healthcare and finance.
Ethical & Security Concerns – AI agents can be manipulated or used maliciously. This raises concerns about data privacy, misinformation, and job displacement.
Why AI agents are the future?
Regardless of above challenges in AI agents, they are the future. We are saying this because of following:
Unmatched Efficiency & Scalability – AI agents automate tasks faster and more accurately than humans. They improve productivity across industries.
Continuous Learning & Adaptation – They are not like traditional software. AI agents learn from data and improve over time. This makes them highly adaptable.
Expanding into Physical & Digital Worlds – AI agents are not just chatbots; they control robots, manage smart cities, and optimize complex systems like supply chains and healthcare diagnostics.
Integration with Most Advanced Tech – AI agents are evolving with LLMs, IoT, and Edge Computing. This will make them more capable and autonomous.
Conclusion
AI agents are no longer just futuristic concepts. They are taking industries towards automation and intelligent decision-making. AI agents are proving their value in real-world applications.
Companies like OrangeMantra are continuously pushing the boundaries of what AI agents can achieve. From past many years, we have been offering AI agent development services for various industries like Retail, Automotive, Manufacturing, BFSI, and more.
The question is no longer “Will AI agents be useful?” but rather “How far can they go?” Businesses that understand the value of AI agents today will be proud at their decision a decade later.
Remember, AI agents are not here to replace humans but to empower them
FAQs
What is the difference between AI and AI agents?
AI is the broad field of creating machines that can think and act intelligently. AI agents are specific applications of AI that can perceive, decide, and act autonomously to achieve goals. Think of AI as the science and AI agents as the “workers” built using that science.
Can AI agents work without human intervention?
Yes, many AI agents are designed to work independently. For example, self-driving cars or chatbots can operate without constant human input. However, they still need occasional updates or oversight.
Are AI agents safe to use?
Generally, yes. But it depends on how they’re designed and used. Proper testing, ethical guidelines, and safeguards are essential to ensure safety. Issues like bias or data privacy can arise if not managed well.
What industries benefit the most from AI agents?
Mostly all. Here are primary ones:
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Finance
- Transportation
- Customer Service
How do AI agents learn and improve over time?
AI agents use machine learning to analyze data, learn patterns, and improve their performance. For example, a recommendation system like Netflix gets better at suggesting shows the more you watch.